
HOW BUSINESS PROCESS DIGITIZATION HELPS SALES
Business systems innovation is the process of identifying a problem(s) in a business environment, finding a solution, and building processes, policies, flows, and operations to support this solution. Development is the process of digitizing these processes and coding them into a software system that automates them.
Automation and “digitization” are subject to absolutely all elements of the business. From production to accounting, from marketing to logistics. From this, the business receives bonuses in the form of expanding its customer base, increasing sales, reducing costs, reducing production costs and increasing profits.
Any company offering products, products or services, operates through specific business processes.
Combining various technologies, you get fundamentally new services.They can simplify life, reduce costs and increase productivity.
The main thing, but at the same time, the most difficult thing in business is interaction with customers or customers. And here includes several processes:
- Creating an effective communication model
- Improving the quality of service
- Analysis of the results and work on possible errors
Each mentioned process requires regular improvements in order to gain more customers, repeat sales and, accordingly, increase profits. And the most effective way to do this is to introduce a CRM system into the business.
Using a CRM-system allows you to always have on hand a ready-made customer base, some of which are ready for re-sales.
In addition if we always view business has a series of processes designed to provide solutions that fill real or perceived needs, then we must always be able to stay two steps ahead of what we see and experience. In other words, the business environment is dynamic. When we discover a need, evaluate, and develop a solution, the environment has already changed. We must be able to get ahead of the curve and predict with certainty the changes happening our business environment.

Creating an effective communication model
If in the traditional model of communications the brand used channels as a tool for broadcasting to the broad masses of the audience, today the brand is becoming part of the consumer communication system and content provider.
The introduction of CRM and new communications reduce customer service costs, increase loyalty and secondary sales, automate electronic payments through terminal networks and sorting goods in stock.
By digitizing systems, we increase customer feedback, and a businesses ability to adapt by integrating into social media and other main forms of communication used by today’s society.
Improving the quality of service
The client communicates with the brand where it is convenient for him.He used to communicate in instant messengers and changing the comfort zone for the sake of buying is not the best option for him.
With digitization of communication, we can operate on multiple channels: We no longer need to retell each other the content of messages and ask again what exactly the customer needs. We can always connect another employee to the communication or redirect the client to more competent colleagues in the matter. For example, during the presentation of a product, a sales manager may forward a technical question to an engineer.
The speed of response and decision making also becomes a key factor in the interaction between the customer and the brand. CRM allows you to control missed calls and receive notifications for the customer to call back. In this case, no client will be lost and the call will not remain unanswered.
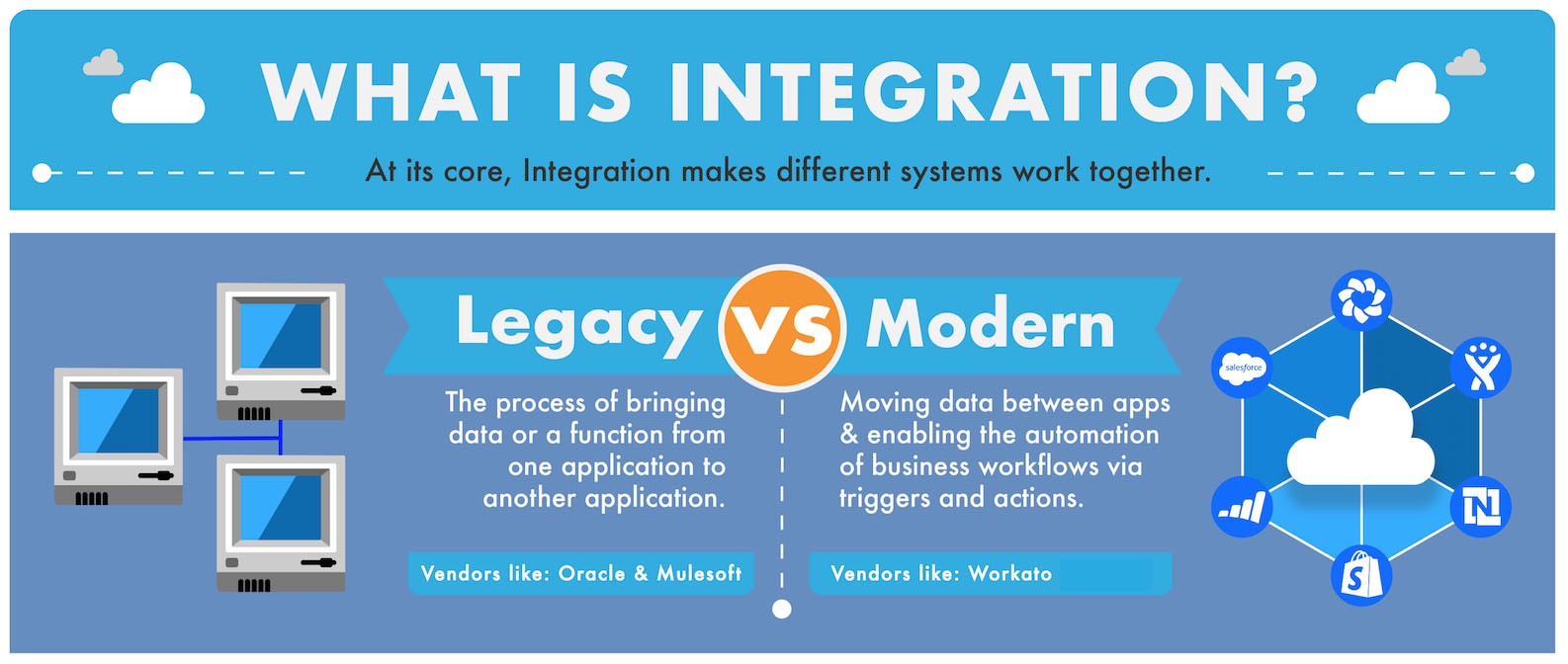
Integration
Sale of goods and products requires integration at all stages of work : the site is integrated with the warehouse program, the statuses and payment processes – from the accounting, delivery – from the logistics, support service – from the call-center. All of these programs act as a single mechanism with online business output.
Analysis of the results and work on possible errors
Information is often the only decision-making tool for improving the quality of service and sales. This requires not only to accumulate data within CRM, but also to analyze it, putting the findings into practice.
The data allows you to analyze the accuracy of your sales funnel, score leads and generally make decisions with greater accuracy.
Transformation of the company’s own culture
Basic automation and patchwork of IT-solutions will never give the same effect, which will provide a comprehensive digitalization of the business . That is why when working with clients through all sales channels it is much more profitable to use CRM and all possible integrations together with constant data analytics. Digitalization of business processes begins with the transformation of processes within the company.
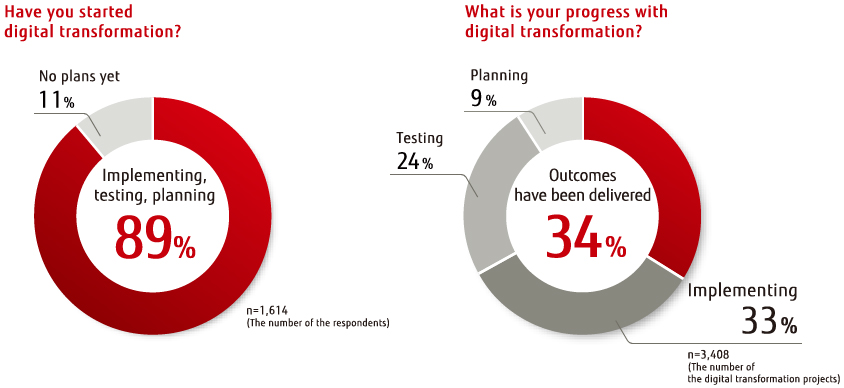
6 success factors for digital business transformation
Digital business transformation is not just another marketing term, it is a new reality that requires a business to radically revise business processes and approaches to working with clients. The ability to quickly adapt to changes and optimize their work “on the fly”, adjusting to the client’s expectations, are the main challenges that the digitalization of the business brings with it.
Customer expectations about the speed and quality of service delivery are growing rapidly. This is especially true of the younger generation of consumers. A high level of service becomes the default requirement. Request for a loan, activation of the service, ordering goods, access to information about expenses, getting advice – customers want to perform all these operations here and now using the devices that they have “at hand”. Consumers increasingly value their time, they need instant feedback, as well as a clear and convenient interface to meet their needs. A good design of information resources, the availability of online chat rooms, an individual approach is a world to which customers have already become accustomed.
In order to meet high customer expectations, companies must speed up the digitization of their business processes. To do this, it is not enough to automate existing business processes. Companies need to reinvent them. The main goals of digital transformation are to increase the speed of decision making, increase the variability of processes depending on the needs and characteristics of the client, and reduce the number of employees involved in the process.
Consumers need instant feedback, as well as a clear and convenient interface to meet their needs.
Digitizing existing processes is an expensive and often quite useless exercise, since all existing problems, shortcomings and crutches are automated. It is necessary to shift the center of gravity towards new opportunities that give the company a competitive advantage. For example, instead of automating the work of employees responsible for working with clients, you need to create self-service systems, minimizing the number of mediators between the client and the final service or product.
Creating digital business processes involves fundamental reengineering and a review of existing constraints. At the initial stage of restructuring, you must select those areas of the process that are related to customer experience. For example, how to reduce the time for making a loan decision from a few days to a few minutes, how to reduce the number of employees involved from X to zero, etc. Below are a few examples from different verticals.
• The bank reduced costs by 70% by introducing an automated mortgage prior approval system. The duration of the procedure was reduced from several days to several minutes.
• The shoe network has implemented an inventory system in its stores, which made it possible to obtain information on the availability of shoe sizes online, which reduced customer waiting times and seller sales at times.
• The insurance company has fully automated the decision-making process for simple operations that take up most of the time of customer service staff. As a result, the number of back office employees involved was drastically reduced.
Digitization of existing processes is an expensive and often rather useless task, since the existing problems and shortcomings are automated.
Another advantage of digitizing business processes is the ability to collect information about customer experience and automatic adaptation of individual process scenarios in accordance with customer expectations. The current level of technology development allows us to fairly accurately predict the needs of customers and the most relevant methods and channels of communication.

Recipes for success in digital transformation of business processes
The human factor, outdated IT systems, lack of knowledge, customer habits are the main obstacles to digital transformation. We offer you 5 recipes that will make the transition to new business processes less complicated, costly and risky.
Leadership support
Digital transformation should be supported and promoted by the top management of the company. This is a prerequisite for the successful implementation of the planned changes. The main task of the leadership is to “sell” (in the good sense of the word) employees innovations and show how they will affect each of them.
New processes can cause job losses for some employees. This fact does not need to be hidden and announced in advance so that the planned changes do not become the subject of rumors and gossip.
Competence center
To implement changes at the operational level, it is necessary to create a cross-functional team consisting of staff members who are responsible for specific aspects of the process. Often, for this purpose, a separate competence center is formed, consisting of employees of various profiles – customer experience designers and designers, marketers, IT representatives, etc. It is important that members of this team are open to new ideas, have the required skills and are not afraid to experiment. Such a center can operate on a regular basis, broadcasting best practices within the company.
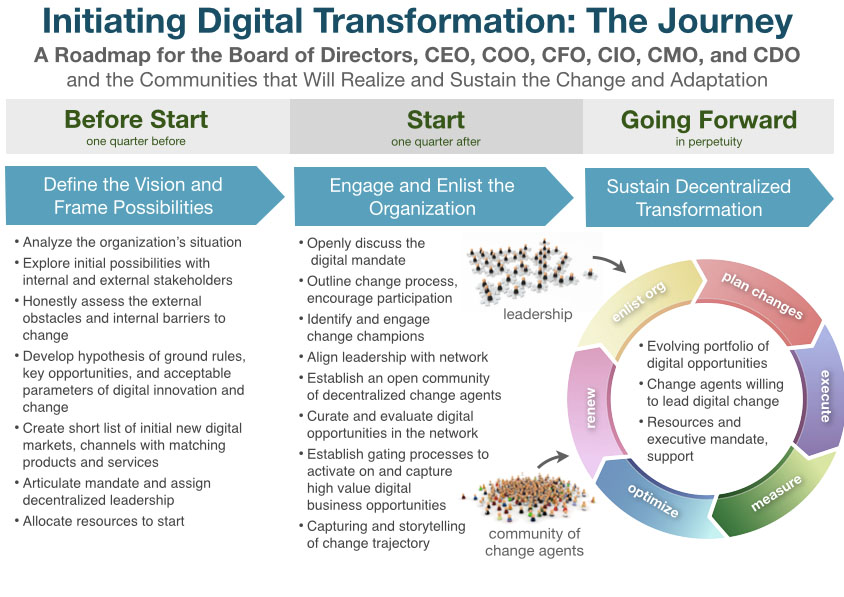
Organizational transformation
Traditionally, new business processes are implemented within the framework of the current organizational structure by employees, which have long been working within existing processes. There are big risks in this approach and here’s why:
• Any innovations take time to learn and adapt. As mentioned above, this always causes a certain rejection among employees. Fears for their work, unwillingness to change established practices, unwillingness to learn, fear of the new – these are traditional attributes of any internal corporate changes.
• When moving to new processes from employees will require more effort. It is necessary to maintain operational efficiency and at the same time switch to the new rules of operation. In fact, employees should “change their shoes” on the go, without changing the speed of movement. It can also create a negative background and cause hidden sabotage or open discontent.
The introduction of new processes by the team working on the old processes is the same as changing the shoes on the move without changing the speed of movement.
Therefore, in some cases it is more appropriate to create a new organizational unit or group within an existing unit to work on new digitized processes.As you migrate to the updated processes, employees of the “old” organizational units will move to a new division. This approach allows you to go through a transformation faster and with less financial and energy efforts.
Evolutionary integration with legacy systems
Digital transformation of business processes affects a large number of legacy-systems, from which it is impossible to get rid of simultaneously. Attempts to integrate old systems into new processes are fraught with long-term projects with vague payback periods. After a few years, it may become clear that what has been done is irrelevant. To reduce these risks, it is important to move in very small steps and “eat an elephant in pieces.” The duration of individual initiatives should not exceed 6 months. Sometimes it makes sense to use simple temporary solutions to move to the “new rails”, in parallel creating integration interfaces between new services and old systems, or completely replacing the latter.
Attempts to integrate old systems into new processes are fraught with long-term projects with vague payback periods.
Customer engagement and promotion
Customer habits are changing slowly, it slows down the introduction of new service technologies. For example, a significant proportion of passengers at train stations stand in line at the cash desk, although terminals for self-purchase of tickets are installed nearby. Fostering new models of consumer behavior is an essential element of digital transformation. It is important to identify key reasons that prevent consumers from starting to use new services and develop measures to involve such customers.Training, demonstration of benefits along with stimulation allows to achieve results. It is important that the first experience of interaction under the new rules be successful and emotionally positive.
Below are a few examples of how this might work:
• Bank employees help office visitors make payments through the terminal.
• The client receives a bonus for making an online application.
• The company offers special conditions for making a purchase through a mobile application.

Flexible business process management model
The classical theory of optimization and reengineering of business processes in new realities is complemented by flexible approaches. The description of business processes, divorced from the business processes themselves, is receding into the past. Such a description is rapidly becoming obsolete; serious labor costs are required to maintain its relevance. The best way to have an up-to-date version of business processes is to use the tools for managing the company’s business processes.
Another characteristic feature of the new approach is a reduction in the duration of the process optimization cycle. The use of A / B testing, control groups and other tools for evaluating changes made allows you to quickly check and implement changes in processes with minimal risks to get negative results.
Top benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing is a big shift from the traditional way businesses think about IT resources. Here are seven common reasons organizations are turning to cloud computing services:

Cost
Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site datacenters—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
Speed
Most cloud computing services are provided self service and on demand, so even vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
Global scale
The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources—for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth—right when it’s needed, and from the right geographic location.
Productivity
On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking”—hardware set up, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more important business goals.
Performance
The biggest cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure data centers, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
Security
Many cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect your data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
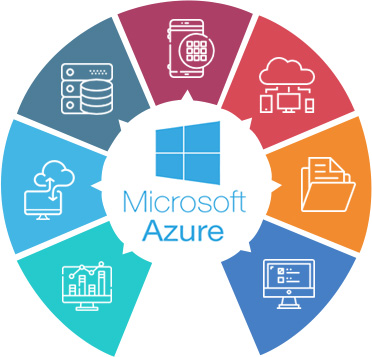
Types of cloud computing
Not all clouds are the same and not one type of cloud computing is right for everyone. Several different models, types, and services have evolved to help offer the right solution for your needs.
Types of cloud deployments: public, private, and hybrid
First, you need to determine the type of cloud deployment, or cloud computing architecture, that your cloud services will be implemented on. There are three different ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud.

Public cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by a third-party cloud services providers which deliver their computing resources like servers and storage over the Internet. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud. With a public cloud, all hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by the cloud provider. You access these services and manage your account using a web browser.
Private cloud
A private cloud refers to cloud computing resources used exclusively by a single business or organization. A private cloud can be physically located on the company’s on-site datacenter. Some companies also pay third-party service providers to host their private cloud. A private cloud is one in which the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, bound together by technology that allows data and applications to be shared between them. By allowing data and applications to move between private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud gives your business
greater flexibility, more deployment options, and helps optimize your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Types of cloud services: IaaS, PaaS, serverless, and SaaS
Most cloud computing services fall into four broad categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), serverless, and software as a service (SaaS). These are sometimes called the cloud computing stack because they build on top of one another. Knowing what they are and how they’re different makes it easier to accomplish your business goals.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
The most basic category of cloud computing services. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Platform as a service refers to cloud computing services that supply an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. PaaS is designed to make it easier for developers to quickly create web or mobile apps, without worrying about setting up or managing the underlying infrastructure of servers, storage, network, and databases needed for development.
Serverless computing
Overlapping with PaaS, serverless computing focuses on building app functionality without spending time continually managing the servers and infrastructure required to do so. The cloud provider handles the setup, capacity planning, and server management for you. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Software as a service is a method for delivering software applications over the Internet, on demand and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure, and handle any maintenance, like software upgrades and security patching. Users connect to the application over the Internet, usually with a web browser on their phone, tablet, or PC.
How cloud computing works
While cloud computing services all work a little differently, many provide a friendly, browser-based dashboard that makes it easier for IT professionals and developers to order resources and manage their accounts. Some cloud computing services are also designed to work with REST APIs and a command-line interface, giving developers multiple options.
Uses of cloud computing
You’re probably using cloud computing right now, even if you don’t realize it. If you use an online service to send email, edit documents, watch movies or TV, listen to music, play games, or store pictures and other files, it’s likely that cloud computing is making it all possible behind the scenes. The first cloud computing services are barely a decade old, but already a variety of organizations—from tiny startups to global corporations, government agencies to non-profits—are embracing the technology for all sorts of reasons.
Here are a few examples of what’s possible today with cloud services from a cloud provider:

Create new apps and services
Quickly build, deploy, and scale applications—web, mobile, and API—on any platform. Access the resources you need to help meet performance, security, and compliance requirements.
Test and build applications
Reduce application development cost and time by using cloud infrastructures that can easily be scaled up or down.
Store, back up, and recover data
Protect your data more cost-efficiently—and at massive scale—by transferring your data over the Internet to an offsite cloud storage system that’s accessible from any location and any device.
Analyze data
Unify your data across teams, divisions, and locations in the cloud. Then use cloud services, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to uncover insights for more informed decisions.
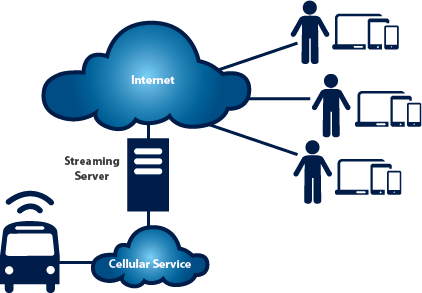
Stream audio and video
Connect with your audience anywhere, anytime, on any device with high-definition video and audio with global distribution.
Embed intelligence
Use intelligent models to help engage customers and provide valuable insights from the data captured.
Deliver software on demand
Also known as software as a service (SaaS), on-demand software lets you offer the latest software versions and updates around to customers—anytime they need, anywhere they are.

Microsoft and cloud computing
Integrated Health Services is an official Microsoft partner and hosts exclusively on Microsoft Azure. Microsoft is a leading global provider of cloud computing services for businesses of all sizes.

